The change control process in the pharmaceutical industry typically involves the following steps:
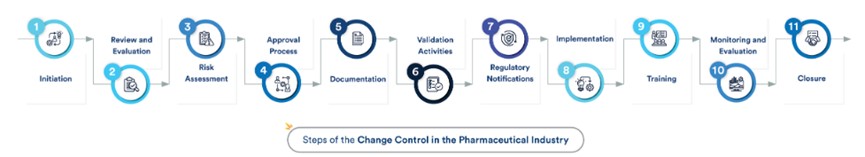
Initiation
Individuals or teams initiate a formal change request, providing details such as the reason for the change, a description of the modification, and the potential impact on product quality.
Review and Evaluation
Relevant stakeholders, including quality assurance, regulatory affairs, and manufacturing, conduct a thorough review of the change request. This includes assessing the impact on product quality, safety, and efficacy.
Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment is performed to identify and evaluate potential risks associated with the proposed change. This step helps in developing strategies to mitigate or manage these risks.
Approval Process
The change request undergoes an approval process. This may involve obtaining approval from various levels of management and may include cross-functional teams.
Documentation
Comprehensive documentation is crucial at every stage of the process. This includes recording the change request details, the rationale for the change, and any decisions made during the review and approval stages.
Validation Activities
Validation activities may be required depending on the nature and significance of the change. This includes testing and studies to ensure the change does not adversely affect product quality, safety, or efficacy.
Regulatory Notifications
For significant changes impacting regulatory submissions or marketing authorizations, notifications or approvals from regulatory authorities may be necessary.
Implementation
The change is implemented in manufacturing once approved and validated. This step involves careful planning and execution to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
Training
Personnel involved in implementing the change are trained to ensure that they understand and can effectively carry out the modified processes or procedures.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential post-implementation. This ensures that the change achieves the desired outcomes and that there are no unexpected consequences. Ongoing assessment helps in refining the process for future changes.
Closure
The change control process is closed once the change has been successfully implemented and all necessary documentation and approvals are in place.
Keys to Managing Change Control Effectively in Life Sciences and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Managing change control in pharmaceutical manufacturing effectively requires establishing robust procedures and policies. Clear, detailed guidelines ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in the change control process. These procedures should outline the steps for initiating, evaluating, approving, and implementing changes.
Involving cross-functional teams is essential for comprehensive change control in pharma. Teams from quality assurance, regulatory affairs, manufacturing, and research and development should collaborate to ensure that all perspectives are considered. This collaborative approach helps identify potential risks and impacts that might not be apparent from a single department's viewpoint.
Training and awareness are critical for effective change control in pharma. Employees must be well-versed in change control procedures and understand the importance of adhering to these protocols. Regular training sessions and updates can help inform everyone about new regulations and best practices.
A robust system for documentation and tracking is vital. Electronic change control systems can enhance efficiency and accuracy by providing a centralized platform for documenting changes, tracking progress, and ensuring all necessary approvals are obtained.
Another key element is conducting thorough risk assessments for each proposed change. Evaluating potential impacts on product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance helps make informed decisions. This step ensures that any risks are identified and mitigated before changes are implemented.
Regular audits and reviews of the change control process help maintain continuous improvement. By evaluating the effectiveness of the change control system and identifying areas for improvement, companies can ensure ongoing compliance and efficiency.
Elements of Change Control in Life Sciences
The change control process typically begins with a formal proposal outlining the change’s need, scope, and potential impacts. This proposal is subjected to a detailed risk assessment and impact analysis to evaluate how the change might affect product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
The approval process involves a thorough review by a cross-functional team, including representatives from quality assurance, regulatory affairs, and other relevant departments. Before giving the go-ahead, this team evaluates the change proposal, considering all potential risks and benefits.
Once approved, a detailed implementation plan is developed. This plan includes timelines, resource allocation, and clearly defined responsibilities to ensure the change is executed smoothly and efficiently.
Testing and validation are critical to ensure that the change does not adversely impact product quality or compliance. This phase involves rigorous testing under controlled conditions to verify that the change produces the desired outcomes without introducing new risks.
Documentation and reporting are essential throughout the change control process. Every change aspect, from the initial proposal to the final implementation, is meticulously documented. This documentation provides a comprehensive record that is invaluable during audits and inspections.
After implementation, a post-implementation review assesses the change's effectiveness. This review ensures that the change has been integrated successfully and functions as intended without any adverse effects. Any issues identified during this phase are addressed promptly to maintain quality and compliance.
Challenges of Change Control in Life Sciences & Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Navigating regulatory complexity is one of the primary challenges in change control. Regulations vary significantly across different regions, making it difficult to ensure compliance on a global scale. Companies must stay abreast of regulatory changes and ensure their change control processes are adaptable to meet diverse regulatory requirements.
Change control processes can be resource-intensive, requiring significant time and effort from multiple departments. This can strain resources, especially in smaller organizations where staff may already be stretched thin. Ensuring adequate staffing and resources to manage change control effectively is a constant challenge.
Resistance to change among employees can also hinder the change control process. Employees may be reluctant to adopt new procedures or technologies due to a lack of understanding or fear of the unknown. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, training, and sometimes a cultural shift within the organization.
Another challenge is managing extensive documentation and ensuring data integrity, particularly with manual systems. Implementing electronic change control systems can help, but transitioning to such systems requires significant investment and training.
Ensuring effective communication and coordination across all departments and stakeholders is critical but challenging. Miscommunication or lack of coordination can lead to delays, errors, and non-compliance. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols is essential for smooth change control processes.
Finally, maintaining continuous compliance during and after changes is crucial. This requires constant vigilance, regular procedure updates, and ongoing training to ensure that all employees remain aware of and adhere to regulatory requirements and best practices.
Service Hotline

 2026 ® Copyright:Titan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Guangdong)
2026 ® Copyright:Titan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Guangdong) 
TOP